Data Engineering Weekly #245
The Weekly Data Engineering Newsletter
A practical guide to building data platforms that grow with you
Scaling Data Teams, the latest in our popular eBook series, is now available. Building and scaling a data platform has never been more important or more challenging. Whether you’re just starting to build a data platform or leading a mature data organization, this guide will help you scale your impact, accelerate your team, and prepare for the future of data-driven products.
Learn how real data teams, from solo practitioners to enterprise-scale organizations, build.
Philipp Schmid: Zero to One: Learning Agentic Patterns
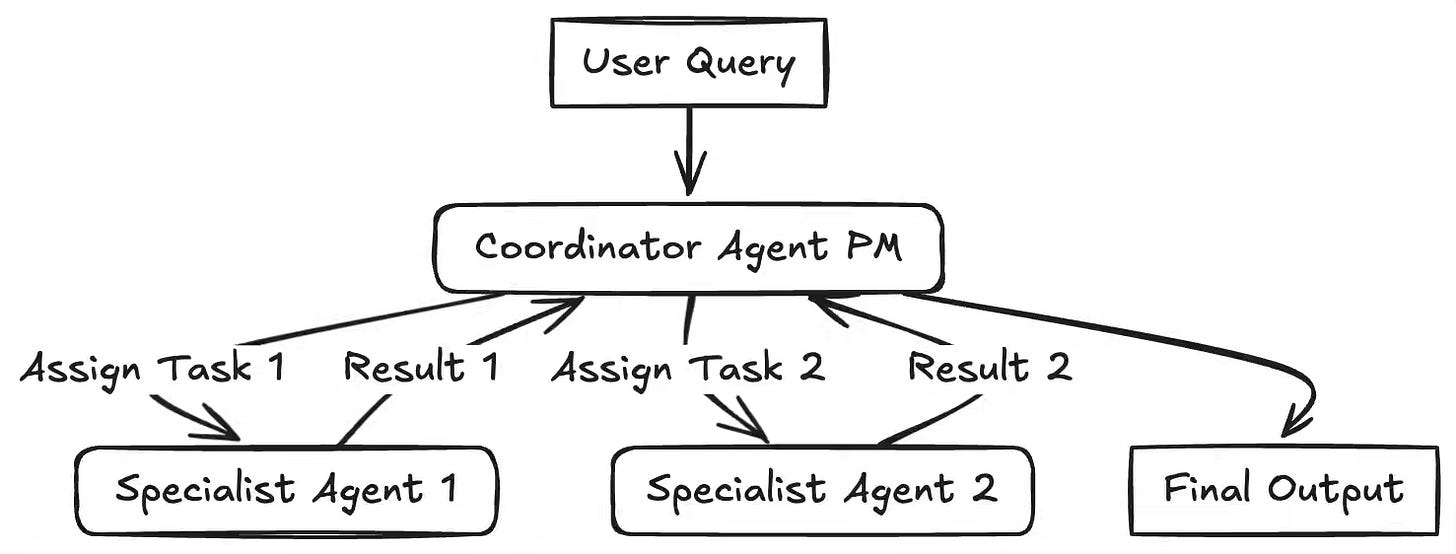
Building reliable AI agents challenges teams to decide when structured workflows suffice versus when dynamic autonomy adds value. The article presents seven foundational design patterns—Prompt Chaining, Routing, Parallelization, Reflection, Tool Use, Planning, and Multi-Agent—that provide modular templates for constructing scalable, adaptable agentic systems. The framework emphasizes the combination and empirical evaluation of these patterns to manage complexity and improve coordination across agents and workflows.
https://www.philschmid.de/agentic-pattern
Gunnar Morling: “You Don’t Need Kafka, Just Use Postgres” Considered Harmful
Engineering teams often oversimplify architecture decisions by suggesting Postgres can replace Kafka for all data needs. The article argues that while Postgres excels as a relational database, it lacks Kafka’s core strengths—persistent logs, consumer groups, low-latency streaming, and rich connector ecosystems—making it unsuitable for event streaming or large-scale data pipelines. Using each system for its intended purpose, with Postgres managing state and Kafka handling real-time events through CDC patterns, yields scalable, reliable, and maintainable architectures.
https://www.morling.dev/blog/you-dont-need-kafka-just-use-postgres-considered-harmful/
Stanislav Kozlovski: Event Streaming is Topping Out
The open source companies built their success on top of open-source platforms, benefited from community contributions and adoption, but now must abandon open-source principles to survive commercially.
The recent news break about “Confluent explores sales” triggered some interesting conversation around the event streaming market and its market cap. The author captures the revenue slide, emerging cloud-native solutions, and other key developments. The key point here is that EMR > Cloudera/ Hortonworks, and MSK > Confluent. It raises a critical question: Are any infrastructure projects safe for hyperscalers? You hardly see a truly open-source license in new infrastructure projects, which is alarming.
https://bigdata.2minutestreaming.com/p/event-streaming-is-topping-out
Sponsored: How PostHog Powers Customer-Facing Web Analytics with Dagster
When PostHog’s enterprise customers couldn’t load their Web Analytics dashboards due to billions of monthly events, the team transformed weekend manual backfills into automated, reliable pipelines that power customer-facing features at scale.
Find out how the PostHog team built their solution with Dagster.
Rohan Virani: Self-play and autocurricula in the age of agents
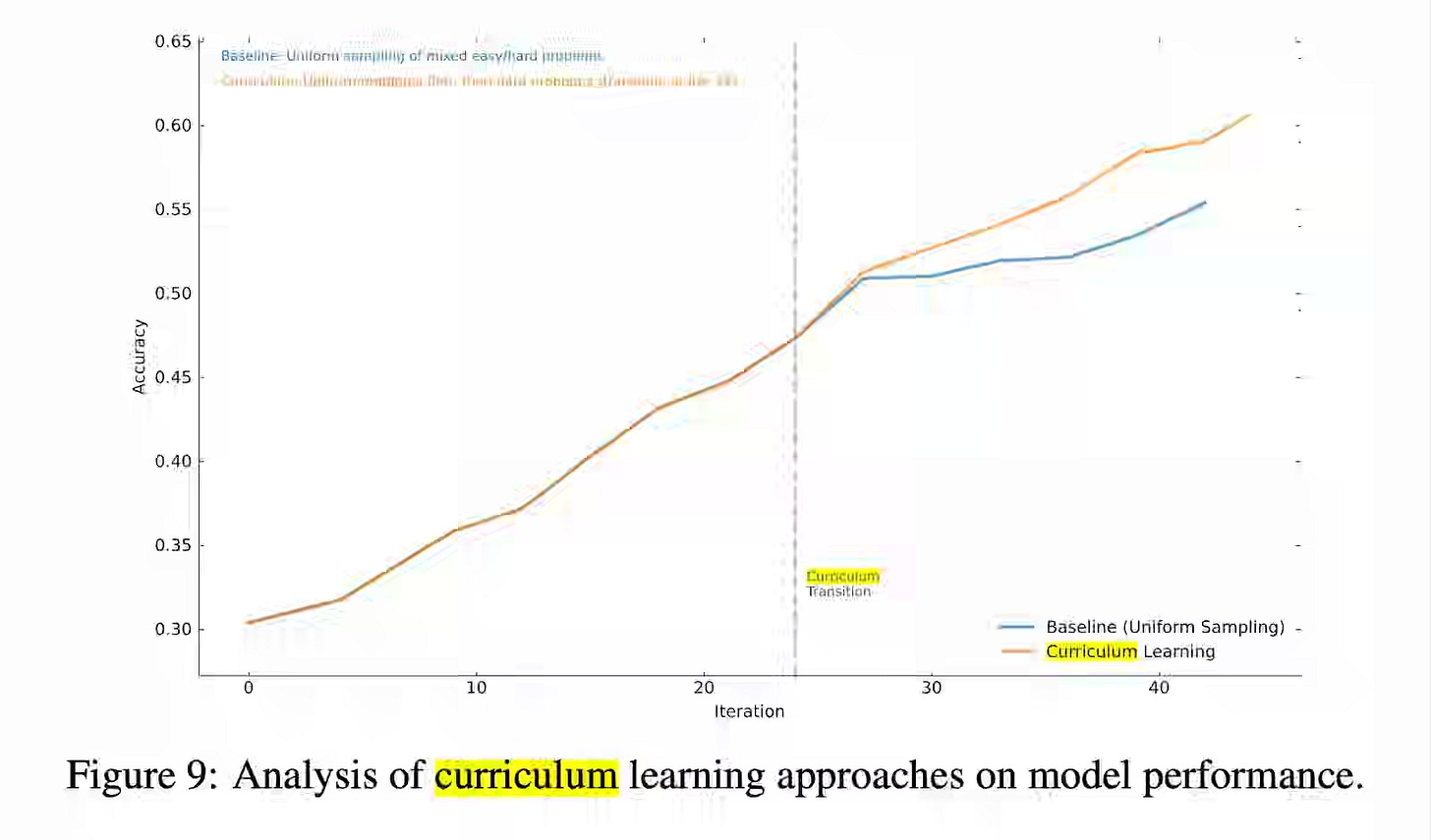
The article surveys methods that target the learnable frontier—curriculum sampling (e.g., LILO), teacher–student self-play (Absolute Zero, SPICE), and unsupervised environment design combined with evolutionary algorithms—to generate learnable, diverse tasks and maintain training stability. Pairing LLM-based environment generators with EAs can improve efficiency and reliability of agent training, but progress depends on tackling reward hacking, long-horizon credit assignment, and robust objective design.
https://www.amplifypartners.com/blog-posts/self-play-and-autocurricula-in-the-age-of-agents
Pinterest: A Decade of AI Platform at Pinterest
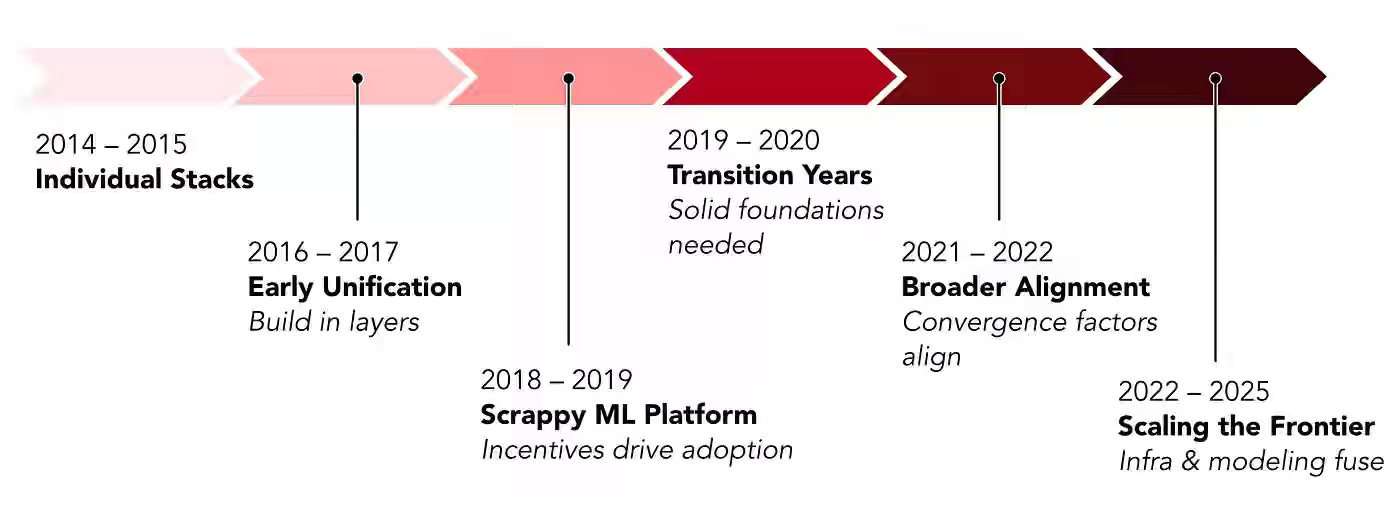
Pinterest writes about a decade-long evolution of its AI platform—from fragmented, team-specific ML stacks causing duplication and brittle pipelines to a unified infrastructure powering all major surfaces. The company matured its platform through five eras: layered unification (Linchpin/Scorpion), foundational resets (UFR and the feature store), and org-backed standardization (MLEnv, TabularML, ML Dataset Store), culminating in GPU- and Ray-based systems for large-scale inference. The platform now serves hundreds of millions of inferences per second with sub-100 ms latency, as MLEnv adoption has risen from under 5% to 95%, and GPU-optimized transformers have boosted Homefeed engagement by 16%.
https://medium.com/pinterest-engineering/a-decade-of-ai-platform-at-pinterest-4e3b37c0f758
Netflix: Supercharging the ML and AI Development Experience at Netflix with Metaflow
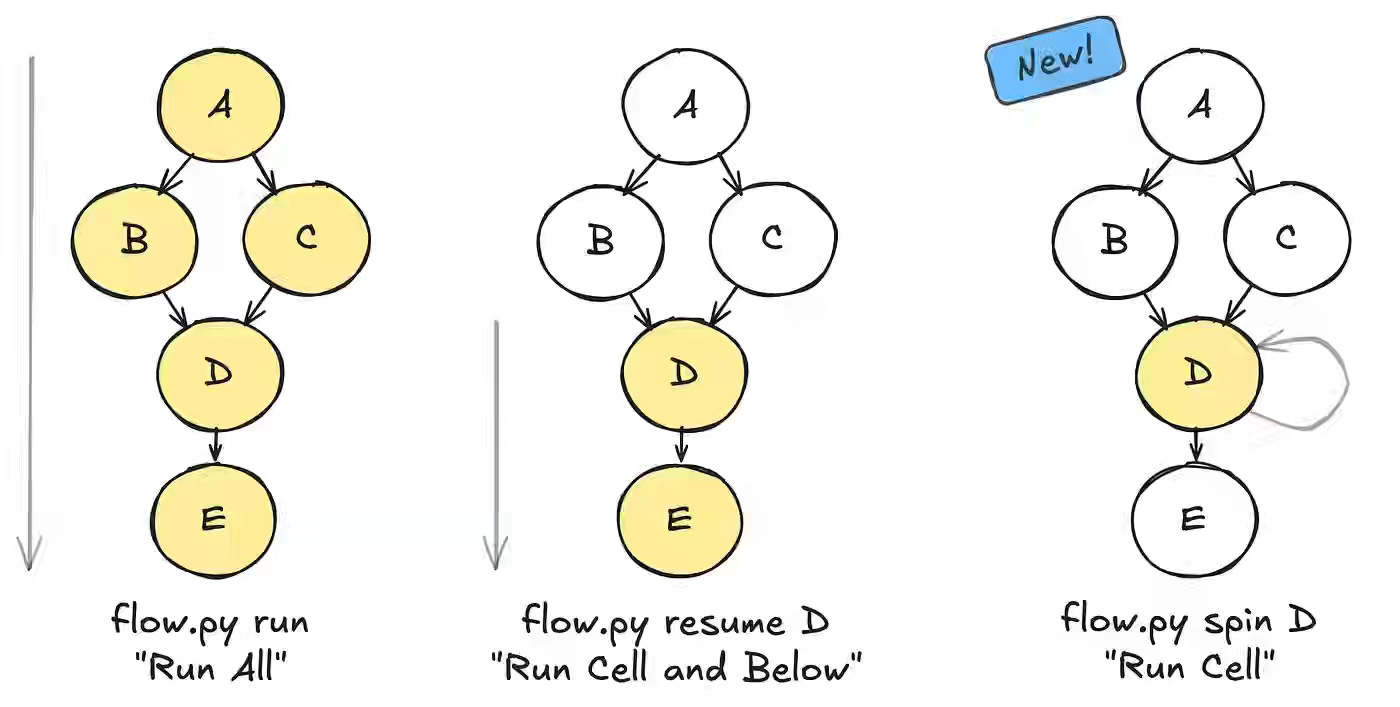
Netflix writes about improving ML and AI developer productivity by addressing slow, state-heavy iteration cycles that made experimentation cumbersome. The new Spin feature in Metaflow 2.19 enables developers to execute individual @steps with preserved state, offering notebook-like interactivity, faster debugging, and integrated visualization through Metaflow Cards in IDEs like VS Code. By combining rapid iteration with production-grade reproducibility, Netflix reports shorter development loops and higher developer velocity across ML and AI systems built on Metaflow and Maestro.
LinkedIn: Accelerating LLM inference with speculative decoding: Lessons from LinkedIn’s Hiring Assistant
LinkedIn writes about tackling high latency in its Hiring Assistant—an AI agent that generates long, structured recruiter responses where conversational speed is critical. The blog discusses n-gram speculative decoding, a lightweight approach that drafts multiple tokens ahead and verifies them losslessly, leveraging recurring phrasing patterns in job–candidate matching to accelerate generation without sacrificing quality. The optimization delivered nearly 4x higher throughput and a 66% reduction in P90 latency, enabling Hiring Assistant to serve complex, global workloads efficiently and at scale while maintaining identical output quality to the base model.
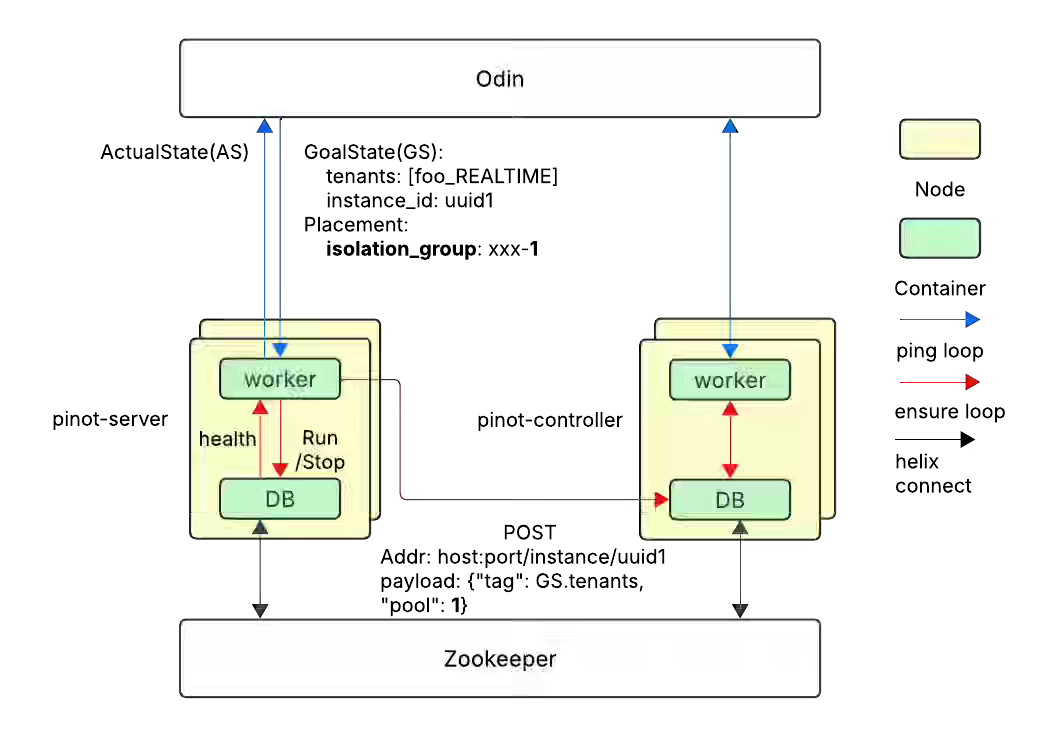
Uber: Building Zone Failure Resilience in Apache Pinot™ at Uber
Uber writes about strengthening Apache Pinot’s reliability for Tier-0 real-time analytics by ensuring clusters remain operational during zone outages. The blog discusses combining pool-based instance assignment and replica-group segment distribution with Uber’s isolation group abstraction to spread data replicas across zones, enabling continuous query and ingestion even when an entire zone fails. The migration—spanning 400+ clusters—was automated via configuration backfills and granular APIs, improving fault tolerance while also cutting Pinot release rollout time from a week to one day through isolation-group-based parallel operations.
https://www.uber.com/en-IN/blog/building-zone-failure-resilience-in-apache-pinot-at-uber/
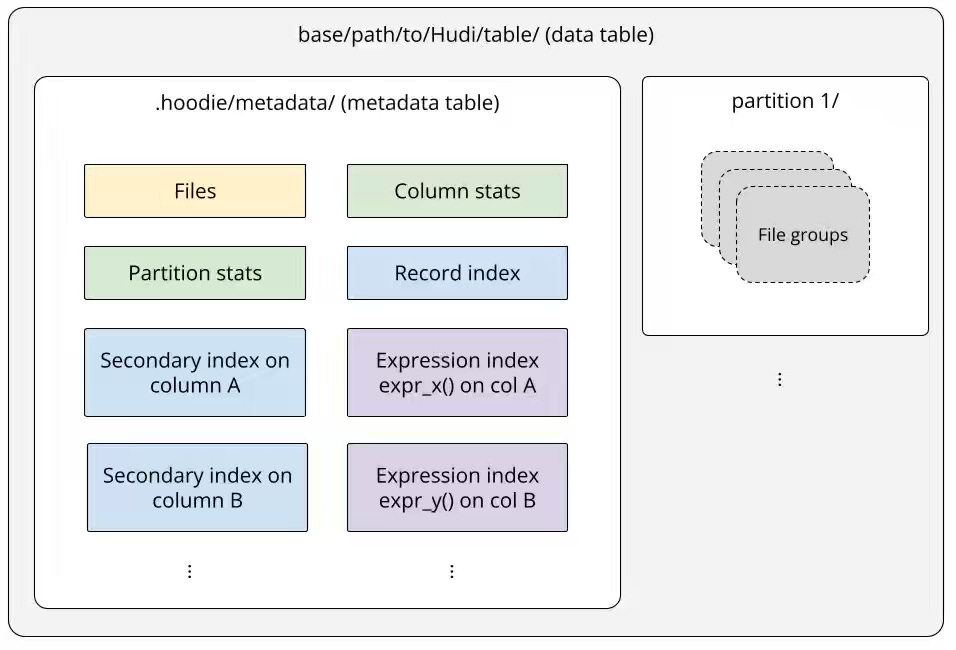
Shiyan Xu: Deep Dive Into Hudi’s Indexing Subsystem (Part 1 of 2)
The author writes about how Apache Hudi extends database-style indexing to the data lakehouse through a self-managed metadata table that powers data skipping and fast record lookups. The metadata table is a Merge-on-Read Hudi table, partitioned by index type (files, column stats, or partition stats), and stored in HFile (SSTable-like) format, enabling efficient key lookups and batched scans. Transactional index maintenance and multi-level data skipping—combining files, partition stats, and column stats indexes—reduce I/O and accelerate queries, achieving up to 93% faster scans on a 1 TB dataset while maintaining consistency and low metadata overhead.
https://hudi.apache.org/blog/2025/10/29/deep-dive-into-hudis-indexing-subsystem-part-1-of-2/
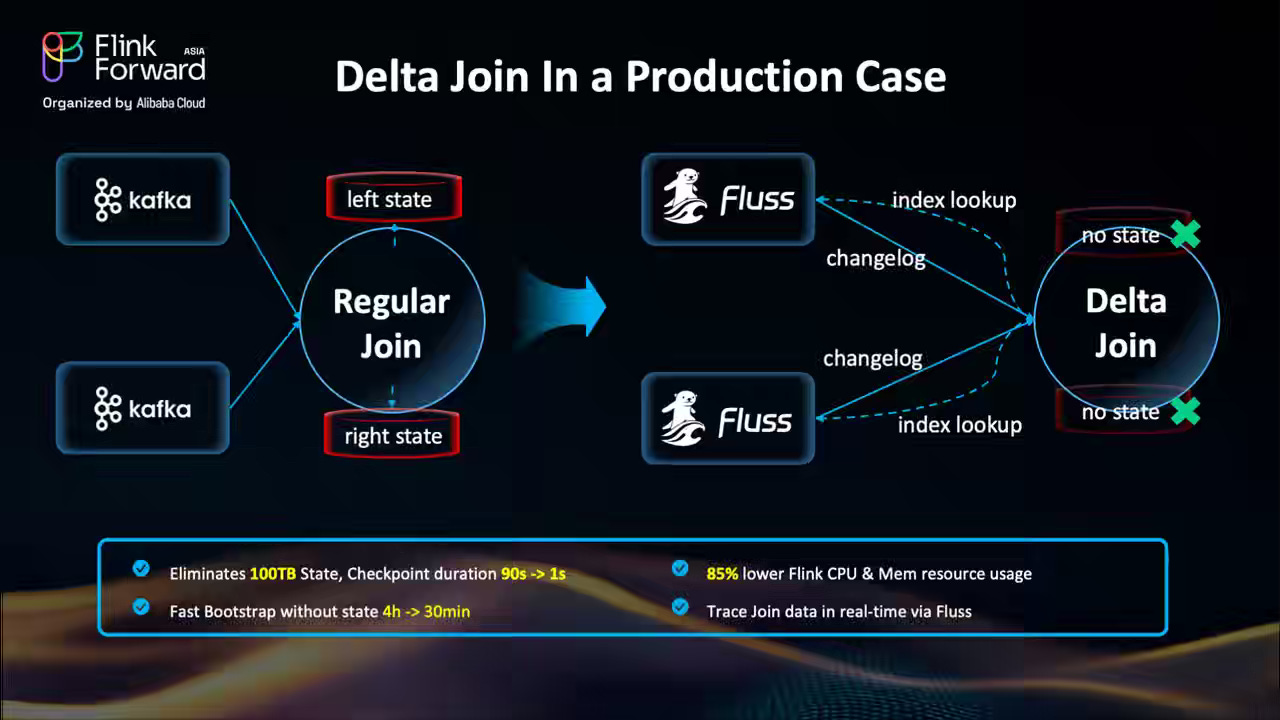
Alibaba: The Delta Join in Apache Flink: Architectural Decoupling for Hyper-Scale Stream Processing
The Apache Flink community writes about Delta Join (FLIP-486), a new join architecture that eliminates unbounded state growth by decoupling compute from historical data in large-scale stream processing. Instead of storing the full join history in Flink’s state, Delta Join performs on-demand lookups against external systems, such as Apache Fluss or Apache Paimon, using asynchronous probes and LRU caching for efficiency. Production deployments demonstrate a 50 TB reduction in join state, a 10× cost reduction, over 80% CPU/memory savings, and a 87% faster recovery, marking a significant shift toward stateless, low-latency joins for real-time analytics at hyper-scale.
All rights reserved, Dewpeche Pvt Ltd, India. I have provided links for informational purposes and do not suggest endorsement. All views expressed in this newsletter are my own and do not represent current, former, or future employers’ opinions.