Data Engineering Weekly #247
The Weekly Data Engineering Newsletter
How to build trustworthy AI analytics
If your team is relying on AI-driven insights, this upcoming webinar will show you how to make those insights more dependable, transparent, and explainable. In this 12/9 Deep Dive with our friends at Cube, you’ll learn:
- Why AI analytics fails without governance (and what that actually means)
- How semantic layers provide the guardrails AI needs to be trustworthy
- Technical implementation: how Compass + Cube work together to prevent hallucinations
- Live demo: governed self-service analytics that data teams can actually trust
DoorDash: Beyond Single Agents: How DoorDash is building a collaborative AI ecosystem
DoorDash highlights the challenge of extracting reliable insights from fragmented knowledge systems and the limitations of single agents constrained by context, determinism, and long-horizon reasoning. The article details an evolutionary architecture that progresses from deterministic workflows to adaptive agents, hierarchical deep-agent systems with shared memory, and exploratory swarm-based A2A collaboration, all built on a unified platform featuring hybrid search, schema-aware SQL generation, multi-stage validation, and integrated guardrails.
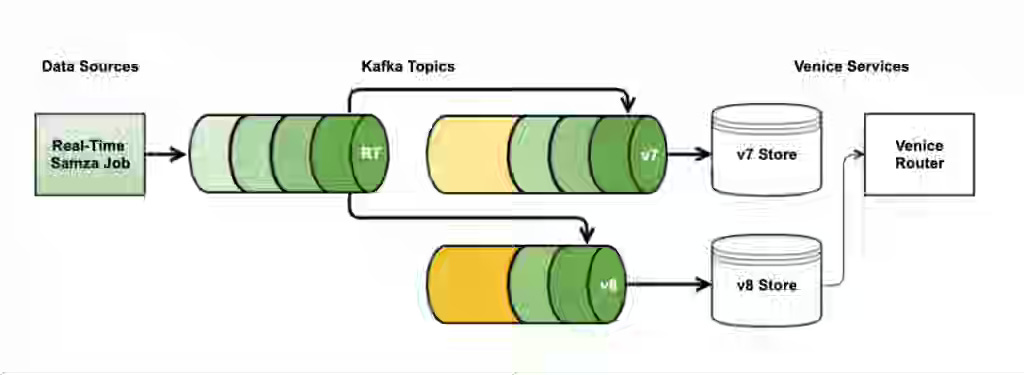
LinkedIn: The evolution of the Venice ingestion pipeline
LinkedIn writes about the challenge of scaling Venice ingestion to support massive bulk loads, hybrid Lambda-style stores, partial updates, and active/active replication while avoiding bottlenecks in producing, consuming, persisting, and compaction. The article details the end-to-end evolution of the ingestion pipeline, including partition scaling, shared consumer and writer pools, SST-based ingestion, RocksDB tuning with leveled compaction, BlobDB, Fast-Avro adoption, parallelized DCR processing, and adaptive throttling for deterministic latency.
https://www.linkedin.com/blog/engineering/infrastructure/evolution-of-the-venice-ingestion-pipeline
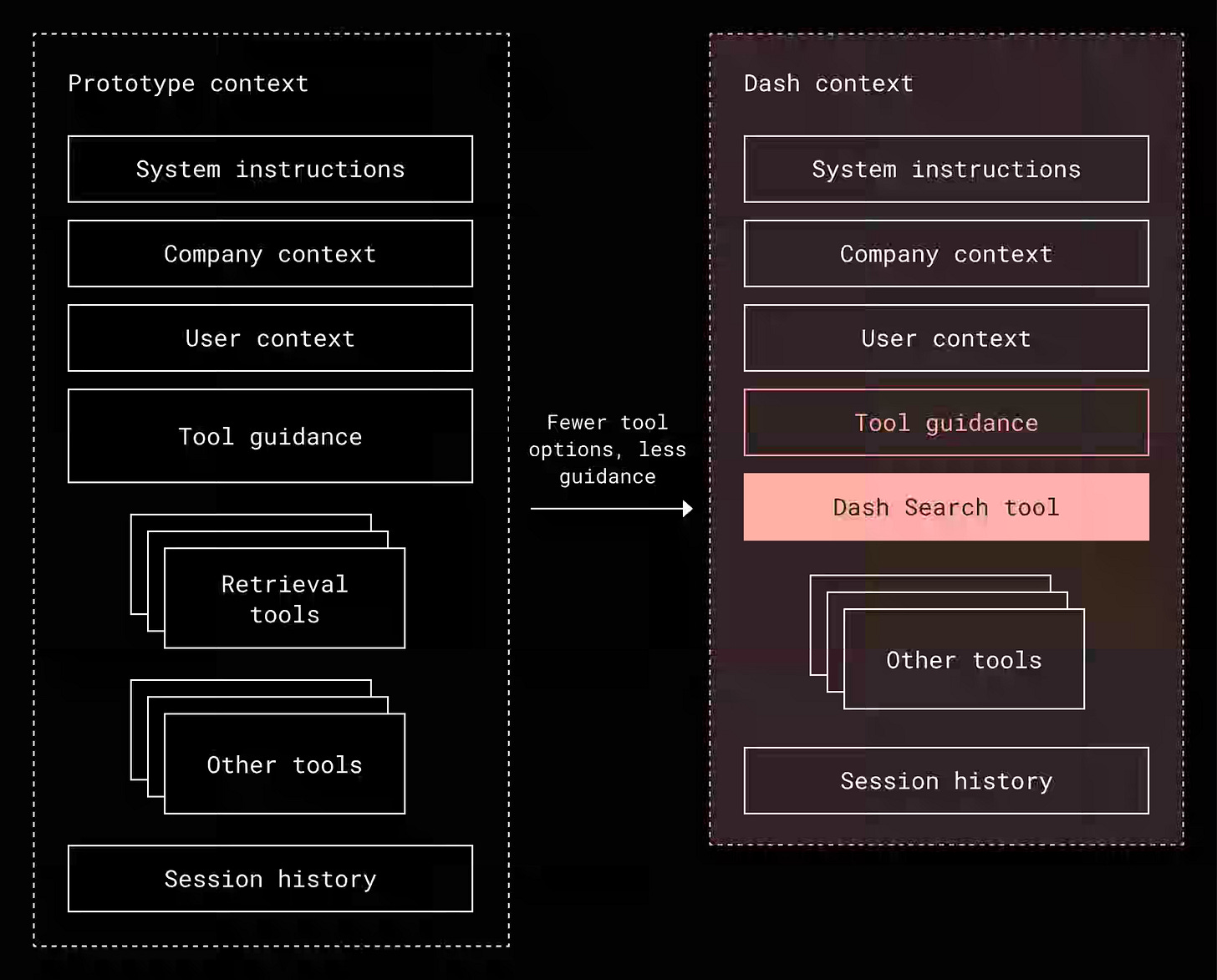
Dropbox: How Dash uses context engineering for smarter AI
Dropbox writes about the transition from a traditional RAG search system to an agentic AI that must reason, plan, and act without being overwhelmed by excessive context, tool proliferation, or accuracy degradation in long-running tasks. The article details three core context-engineering strategies:
Consolidating retrieval into a single universal search tool
Filtering context through a unified index and knowledge graph for relevance.
Delegating complex workflows, such as query construction, to specialized agents with focused prompts.
The approach improves reasoning quality, reduces token and decision overhead, and enables faster, more accurate agentic execution across Dash’s growing AI capabilities.
https://dropbox.tech/machine-learning/how-dash-uses-context-engineering-for-smarter-ai
Sponsored: The guide to scaling your data team
Scaling Data Teams, the latest in our popular eBook series, is now available. Building and scaling a data platform has never been more important or more challenging. Whether you’re just starting to build a data platform or leading a mature data organization, this guide will help you scale your impact, accelerate your team, and prepare for the future of data-driven products.
Learn how real data teams, from solo practitioners to enterprise-scale organizations, build.
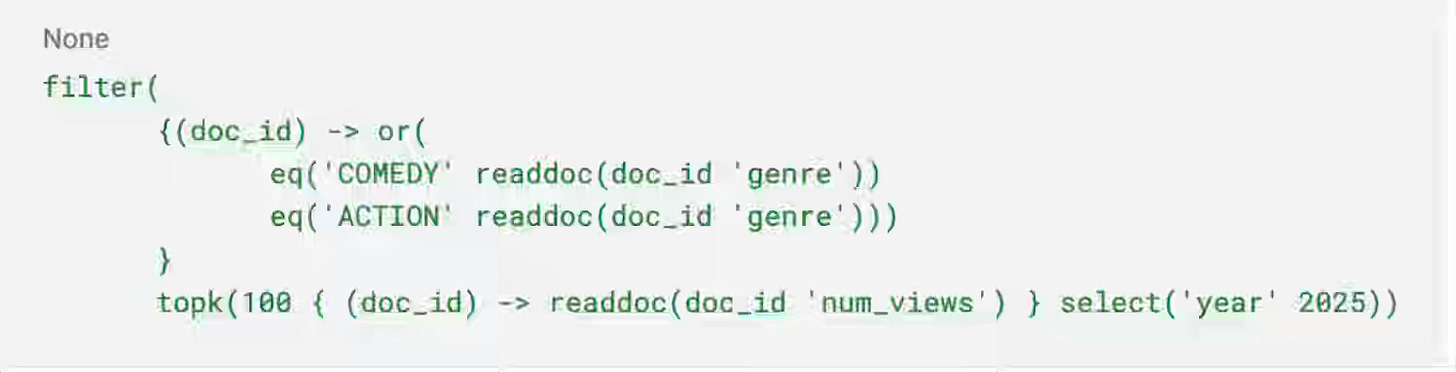
LinkedIn: FishDB - a generic retrieval engine for scaling LinkedIn’s feed
LinkedIn writes about replacing its legacy Java-based feed infrastructure with FishDB, a custom Rust-based retrieval engine designed to eliminate Garbage Collection latency and reduce memory overhead by ~5x compared to JVM equivalents. By leveraging a lambda architecture for ingestion and graph-based document references for query execution, FishDB cut hardware usage by 50% while maintaining a strict 40ms p99 latency. The query language is very interesting, improving expressiveness, and it suits the retrieval engine well.
Netflix: Integrating Netflix’s Foundation Model into Personalization applications
Netflix writes about integrating the personalization Foundation Model into diverse production systems that have different latency constraints, feature pipelines, and appetites for model complexity. The article details three integration patterns: using stable daily embeddings via the Embedding Store, embedding the Foundation Model as a fine-tunable subgraph within downstream models to provide fresh representations, and fully fine-tuning the Foundation Model to power product-specific objectives directly.
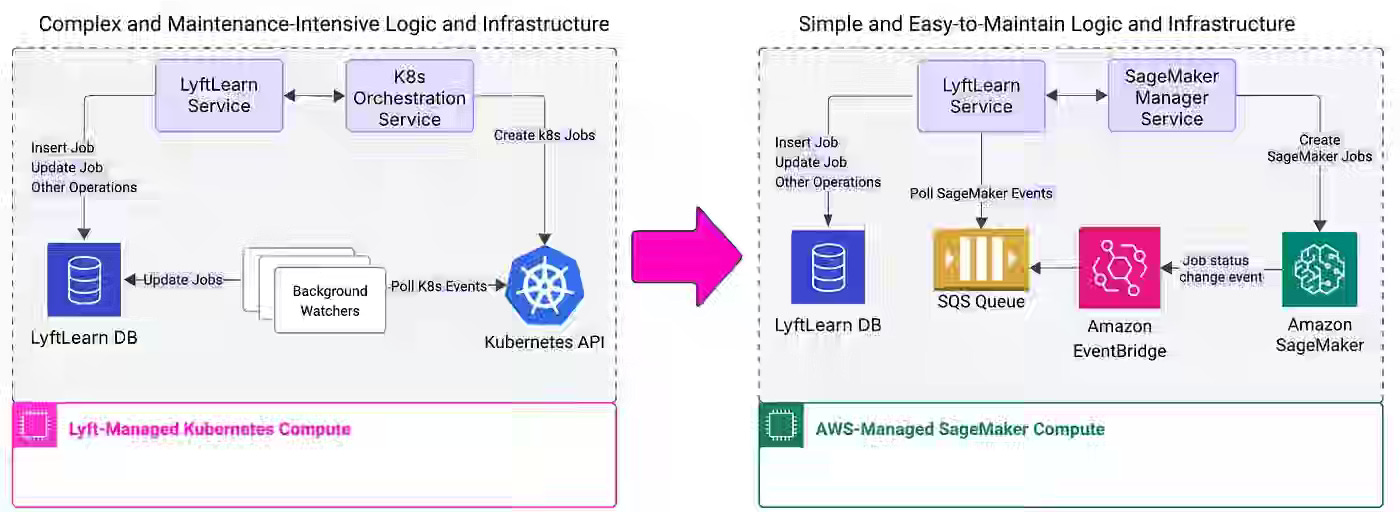
Lyft: LyftLearn Evolution: Rethinking ML Platform Architecture
Lyft writes about the challenge of scaling its Kubernetes-only LyftLearn ML platform as operational complexity, state management overhead, and cluster-level capacity tuning become bottlenecks for thousands of daily training jobs and notebooks. The article details a hybrid LyftLearn 2.0 architecture that keeps low-latency online serving on Kubernetes while moving offline compute to AWS SageMaker, enabled by cross-platform base images, a SageMaker manager service, and SQS/EventBridge–based state tracking.
https://eng.lyft.com/lyftlearn-evolution-rethinking-ml-platform-architecture-547de6c950e1
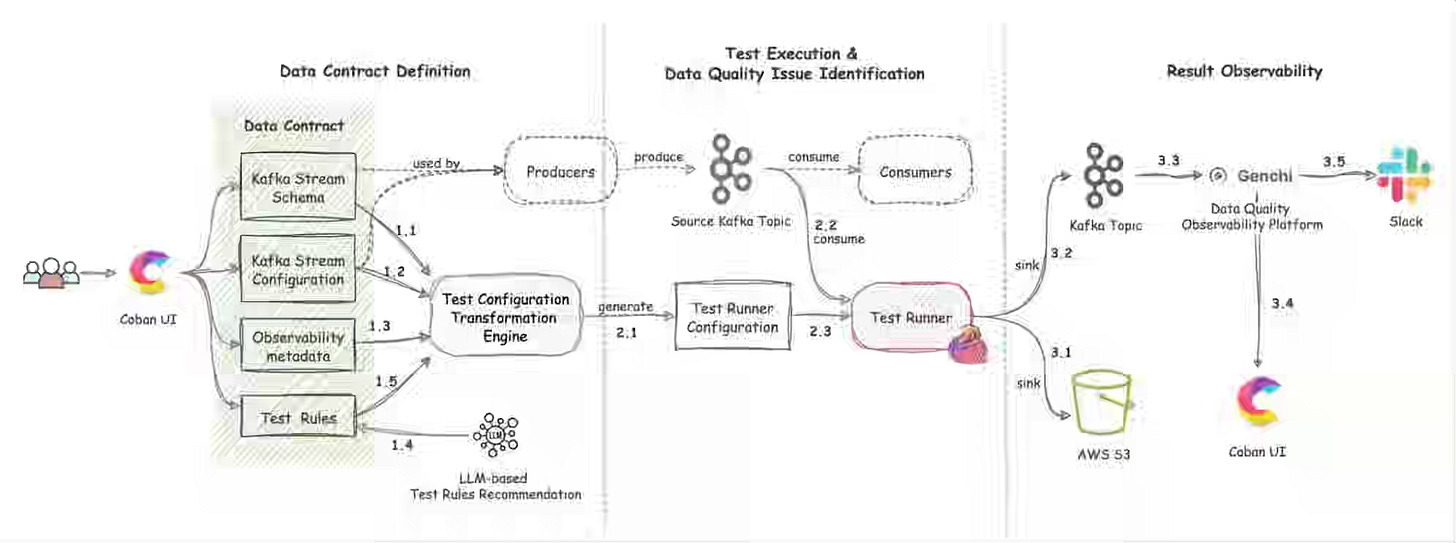
Grab: Real-time data quality monitoring: Kafka stream contracts with syntactic and semantic test.
Grab writes about implementing a data contract in a real-time streaming engine with syntactic and semantic tests. The blog is essentially a testimonial for data contract frameworks and their role as an integral part of data pipeline engineering.
https://engineering.grab.com/real-time-data-quality-monitoring
BlaBlaCar: Why We Built “BlaBlaCar Data Copilot”: Shifting Data Analysis Left
BlaBlaCar writes about the bottleneck created by a hard boundary between software engineers and data analysts, where engineers avoid the warehouse, and analysts drown in ad hoc questions and fragile SQL, slowing feedback on product data and undermining true data ownership. The article presents BlaBlaCar Data Copilot, an AI-powered “junior analyst” inside the IDE that tunnels into BigQuery, uses curated queries and table previews via a lightweight zero-infrastructure RAG pattern, generates SQL/Python plus data health cards, and turns analyses into tested scripts reviewed via pull requests and stored as long-term repo memory.
Vinted: Dense Retrieval
The blog describes how low recall keyword searches on a highly visual, multilingual e-commerce catalog led to missed business opportunities and made it hard to safely roll out dense retrieval at scale under tight latency and consistency constraints. The article details a CLIP-based two-tower dense retrieval model trained with large-scale contrastive learning, exported to ONNX and embedded into a Vespa-based architecture, plus a long list of optimizations including index sharding by market, tuned ANN thresholds, approximate→exact retry strategies, global-phase reciprocal rank fusion to cap NN matches, and JVM tuning with GraalVM and ZGC.
https://vinted.engineering/2025/11/18/dense-retrieval/
All rights reserved, Dewpeche Pvt Ltd, India. I have provided links for informational purposes and do not suggest endorsement. All views expressed in this newsletter are my own and do not represent current, former, or future employers’ opinions.






Excellent roundup, especially the Vinted dense retrieval piece. The index sharding-by-market strategy they disscuss is clever because it sidesteps the global coordination overhead thatmost dense retrieval implementations trip over at scale. Geographic partitioning feels obvious in hindsight but combining that with their reciprocal rank fusion in the global phase is what really makes the whole setup work under tight latency budgets.